Updated at 2022-01-29
Link
Introduction
달라진 풀이 스타일을 적용하여 다시 풀어보았다. 이번에는 종이, 펜 그리고 손가락 두 개를 가지고 시뮬레이션을 한다.
슬라이딩 윈도우를 적용한 이 풀이는 Sliding Window에서 다룬 내용을 참고하여 진행한다.
Note
- python에서 % 연산자를 사용해 어떤 숫자를 10으로 나눈 나머지를 구할 때는 소수점이 붙는 경우가 있으므로 주의
- (ex) 1 -> 1.0, 0 -> 0.0)
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
import math
from collections import deque
def convert_no(n, k):
nums, quotient = deque(), n
while quotient > 0:
quotient, remainder = quotient // k, int(quotient % k)
nums.appendleft(str(remainder))
return ''.join(nums)
def is_prime_no(no):
if no < 2:
return False
offset = int(math.sqrt(no)) + 1
for i in range(2, offset):
if no % i == 0:
return False
return True
def contain_zero(no):
return True if '0' in str(no) else False
def solution(n, k):
answer = 0
no = convert_no(n, k)
left, right = 0, 0
while right < len(no):
if no[right] == '0':
cur_no = int(no[left:right])
if is_prime_no(cur_no) and not contain_zero(cur_no):
answer += 1
left = right = right + 1
if right == len(no) - 1: # 5
cur_no = int(no[left:])
if is_prime_no(cur_no) and not contain_zero(cur_no):
answer += 1
right += 1
return answer
풀이
1, 어떤 수의 k진수를 구하는 법은 그 수를 k로 나누며 0이 될 때까지 나누고 나머지를 이어주면 된다.
ex) 35를 2진수로 표현하는 방법
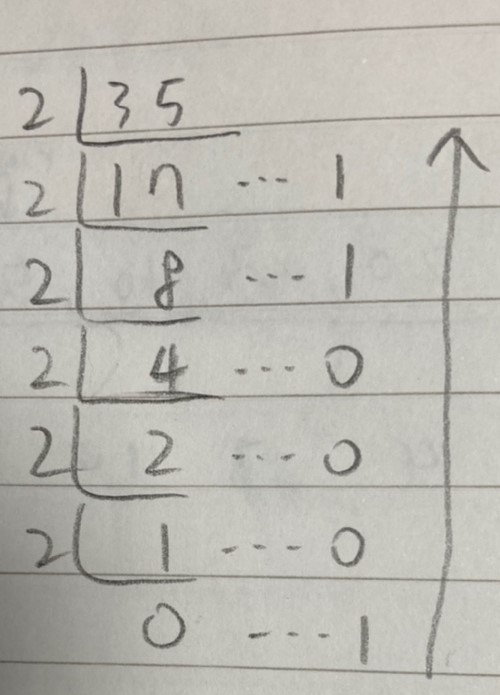
35 —2진수로 변환—> 100011(2)
이를 구현한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
from collections import deque
def convert_no(n, k):
nums, quotient = deque(), n
while quotient > 0:
quotient, remainder = quotient // k, int(quotient % k)
nums.appendleft(str(remainder))
return ''.join(nums)
def solution(n, k):
no = convert_no(n, k) # 1
2, 이렇게 변환된 숫자를 종이에 쓰고 왼쪽 검지와 오른쪽 검지를 숫자 가장 첫 번째 위치(인덱스 0)에 둔다. 우리는 이 오른쪽 손가락을 숫자의 끝자락까지 움직일거다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
from collections import deque
def convert_no(n, k):
nums, quotient = deque(), n
while quotient > 0:
quotient, remainder = quotient // k, int(quotient % k)
nums.appendleft(str(remainder))
return ''.join(nums)
def solution(n, k):
no = convert_no(n, k)
left, right = 0, 0
while right < len(no): # 2
right += 1
3, 자 이제 손가락을 움직이면서 손가락 사이의 글자를 체크할 건데, 생각을 해본다. 우리는 언제 숫자를 체크해야 하나? 바로 0과 0 사이에 숫자가 존재할 때이다.
즉, 오른쪽 손가락이 0인 지점에 멈췄을 때 손가락 사이의 숫자를 체크하면 된다. (편의상 손가락 사이라는 표현을 했지만 실제로는 왼쪽 손가락이 가리키는 글자까지 포함해서 센다.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
from collections import deque
def convert_no(n, k):
nums, quotient = deque(), n
while quotient > 0:
quotient, remainder = quotient // k, int(quotient % k)
nums.appendleft(str(remainder))
return ''.join(nums)
def solution(n, k):
no = convert_no(n, k)
left, right = 0, 0
while right < len(no):
if no[right] == '0': # 3
cur_no = int(no[left:right])
right += 1
4, 문제의 조건에 따르면 숫자는 각 자릿수에 0을 포함하지 않는 소수이다. 소수이며, 0을 포함하지 않는다.
3번에서 고른 숫자들을 이 기준에 따라 체크한다. 체크 후에는 양 손가락을 방금 오른쪽 손가락이 있던 바로 다음 위치로 옮겨준다.
소수는 1과 자기 자신으로 밖에 나누지 못한다. 즉 1과 자기 자신 이외의 약수를 가지지 않는 수인데, 이 약수를 빠르게 구하는 법을 다 담으면 포스팅이 너무 길어져서 괜찮은 다른 블로그의 링크를 대신한다. (구글에서 약수 찾는 알고리즘 쳐서 제일 위에 나오는 거 링크 걸었다.)
스포일러 하자면, 그 숫자의 제곱근까지만 약수가 되는지 체크해보면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
import math
from collections import deque
def convert_no(n, k):
nums, quotient = deque(), n
while quotient > 0:
quotient, remainder = quotient // k, int(quotient % k)
nums.appendleft(str(remainder))
return ''.join(nums)
def is_prime_no(no):
if no < 2:
return False
offset = int(math.sqrt(no)) + 1
for i in range(2, offset):
if no % i == 0:
return False
return True
def contain_zero(no):
return True if '0' in str(no) else False
def solution(n, k):
answer = 0
no = convert_no(n, k)
left, right = 0, 0
while right < len(no):
if no[right] == '0':
cur_no = int(no[left:right])
if is_prime_no(cur_no) and not contain_zero(cur_no): # 4
answer += 1
left = right = right + 1
right += 1
5, 오른쪽 손가락이 마지막 지점까지 갔을 때 그 숫자가 0이 아니면 마지막 손가락 사이의 소수는 체크가 되지 않는다. 따라서 이 경우에는 현재 왼쪽 손가락 부터 앞에 있는 모든 숫자를 체크해준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
import math
from collections import deque
def convert_no(n, k):
nums, quotient = deque(), n
while quotient > 0:
quotient, remainder = quotient // k, int(quotient % k)
nums.appendleft(str(remainder))
return ''.join(nums)
def is_prime_no(no):
if no < 2:
return False
offset = int(math.sqrt(no)) + 1
for i in range(2, offset):
if no % i == 0:
return False
return True
def contain_zero(no):
return True if '0' in str(no) else False
def solution(n, k):
answer = 0
no = convert_no(n, k)
left, right = 0, 0
while right < len(no):
if no[right] == '0':
cur_no = int(no[left:right])
if is_prime_no(cur_no) and not contain_zero(cur_no):
answer += 1
left = right = right + 1
if right == len(no) - 1: # 5
cur_no = int(no[left:])
if is_prime_no(cur_no) and not contain_zero(cur_no):
answer += 1
right += 1
return answer
Legacy
지난 풀이.
- 주어진 수를 n진수로 변환한다.
- 커서를 두 개 두고 하나를 전진시키면서 커서 사이의 숫자가 소수이면서 0이 포함되어 있지 않다면 정답에 포함시키고 두 커서의 위치를 다음 숫자로 옮긴다.
- 110011 같이 11을 정답에 포함시킨 후 left, right 커서들의 위치가 index 3인 0에(110011) 위치하는 경우가 있다. 이 때는 커서들을 index 4인 1로(110011) 옮겨준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
import math
from collections import deque
def convert_no(n, k):
nums, quotient = deque(), n
while quotient > 0:
quotient, remainder = quotient // k, int(quotient % k)
nums.appendleft(str(remainder))
return ''.join(nums)
def is_prime_no(no):
if no < 2:
return False
offset = math.floor(math.sqrt(no)) + 1
for i in range(2, offset):
if no % i == 0:
return False
return True
def contain_zero(no):
return True if '0' in str(no) else False
def solution(n, k):
answer, left, right = [], 0, 0
no = convert_no(n, k)
while right < len(no):
if no[right] == '0':
if left == right:
left = right = right+1
else:
cur_no = int(no[left:right])
if is_prime_no(cur_no) and not contain_zero(cur_no):
answer.append(cur_no)
left = right+1
elif right == len(no)-1:
cur_no = int(no[left:])
if is_prime_no(cur_no) and not contain_zero(cur_no):
answer.append(cur_no)
right += 1
return len(answer)
Comment
코테에 시간제한이 있어야 변별력이 있겠지만 없었으면 좋겠다. 난 같은 코드를 진득하니 보면서 계속 깔끔하게 다듬어나가는 걸 좋아하는데 시간제한이 있으면 너무 허겁지겁 푸느라 가독성이 개판이 되어버린다.
아직 실력이 부족해서 한 번에 깔끔한 코드를 못 짜서 그런거겠지?
2022-01-29 내용 추가
달라진 문제 풀이 스타일 덕분에 이 문제가 어느정도 해결될 것 같은 조짐이 보인다. 뭔가 희망이 생겼다.
