Link
Introduction
다익스트라 알고리즘은 포스트로 하나쯤은 정리해둬야 겠다고 생각했는데 딱 이 문제가 눈에 들어왔다.
N개의 마을 중 1번 마을에서부터 K시간 이하로 배달이 가능한 마을을 전부 찾는 이 문제는 각 노드들 간의 최단거리를 구하는 전형적인 다익스트라 알고리즘 문제이다.
다익스트라 알고리즘은 한 노드를 기준으로 이어져 있는 모든 노드를 힙에 넣어 가까운 거리순으로 정렬하고, 힙에서 하나씩 꺼내서 방문하며 거리를 갱신하는 방식으로 각 정점별 거리들을 기록하는 DFS의 일종이다.
이를 정말 간결하고 이해하기 쉬운 방식으로 구현해둔 블로그를 찾아서 그 링크를 남긴다. 이번 풀이에서도 다익스트라 탐색은 해당 구현방식을 차용했다.
(이 구현방식은 정말 직관적이며, 이해하기에도 어렵지 않은 뛰어난 방식이다.)
Python으로 다익스트라(dijkstra) 알고리즘 구현하기 at justkode
Note
- 처음 방문 그래프를 만들 때, 선택한 두 개의 노드 사이에 간선이 2개 이상 있는 경우 더 짧은 거리로 갱신한다.
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
import heapq
from collections import defaultdict
def djikstra(graph, start):
distances = {node:float('inf') for node in graph}
distances[start] = 0
heap = [[distances[start], start]]
while heap:
distance, destination = heapq.heappop(heap)
if distance > distances[destination]:
continue
for next_destination, next_distance in graph[destination].items():
new_distance = distance + next_distance
if new_distance < distances[next_destination]:
distances[next_destination] = new_distance
heapq.heappush(heap, [new_distance, next_destination])
return distances
def create_graph(road):
graph = defaultdict(dict)
for r in road:
start, end, distance = r
if start in graph and end in graph[start]:
distance = min(graph[start][end], distance)
graph[start][end] = distance
graph[end][start] = distance
return graph
def solution(N, road, K):
graph = create_graph(road)
distances = djikstra(graph, 1)
answer = 0
for destination, distance in distances.items():
if distance <= K:
answer += 1
return answer
풀이
1. 필요한 함수 정의
우선 노드별 거리 정보가 담긴 그래프를 생성하는 함수를 정의하고 이 그래프와 시작점을 정하면 각 노드까지의 거리들을 반환하는 함수를 정의한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
def djikstra(graph, start):
pass
def create_graph(road):
pass
def solution(N, road, K):
graph = create_graph(road)
distances = djikstra(graph, 1)
2. 노드별 거리 그래프 생성
우선 딕셔너리(해쉬맵)로 노드간의 거리 정보가 담긴 그래프를 구현하여 사용한다. (ex. graph[1][4] = 3)
그래프에는 선택된 노드 두 개(start, end)의 서로 같은 거리를 넣어준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
from collections import defaultdict
def create_graph(road):
graph = defaultdict(dict)
for r in road: # 2-1
start, end, distance = r
graph[start][end] = distance
graph[end][start] = distance
return graph
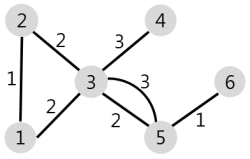
그런데 지도 그림을 보니 같은 노드 사이에 간선이 2개인 경우도 있다. 간선이 2개인 경우 더 작은 거리를 가진 간선의 거리를 선택하도록 수정해준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
from collections import defaultdict
def create_graph(road):
graph = defaultdict(dict)
for r in road:
start, end, distance = r
if start in graph and end in graph[start]: # 2-2
distance = min(graph[start][end], distance)
graph[start][end] = distance
graph[end][start] = distance
return graph
이렇게 모든 노드가 자신과 이어진 노드들과의 거리 값을 모두 기록하고 있는 그래프가 완성되었다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
{
"1": { "2": 1, "4": 2 },
"2": { "1": 1, "3": 3, "5": 2 },
"3": { "2": 3, "5": 1 },
"4": { "1": 2, "5": 2 },
"5": { "2": 2, "3": 1, "4": 2 }
}
3. 다익스트라 알고리즘으로 탐색
djikstra() 함수의 목표는 그래프와 시작점을 넣어주면 시작점에서부터 모든 노드들을 탐색하여 각 노드까지의 거리를 담고 있는 distances라는 딕셔너리를 반환하는 것이다.
이를 위해 distances라는 이름으로 {노드:거리}의 딕셔너리를 만든다. 이 때, 거리 값은 무한대로 초기화한다.
1
2
3
4
import heapq
def djikstra(graph, start):
distances = {node:float('inf') for node in graph} # 3-1
첫 번째 노드의 거리를 0으로 설정하고 heap에 [거리, 목적지]순으로 넣어준다.
인자로 받은 시작점부터 탐색할 것이기 때문에 목적지로 시작점을 넣어준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
import heapq
def djikstra(graph, start):
distances = {node:float('inf') for node in graph}
distances[start] = 0 # 3-2
heap = [[distances[start], start]] # 3-2
heap에서 거리와 목적지를 차례로 꺼내서 현재 노드까지의 거리와 목적지의 거리를 더한 후 이 값이 원래 distances에 있는 값보다 크다면 무시하고 작다면 갱신해주고 해당 노드를 최단거리순 방문예정 리스트인 heap에 넣어준다.
뭔가 복잡해보이지만 별거 없다. distances를 갱신한다는 목표만 잊지 않고 있으면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
import heapq
def djikstra(graph, start):
distances = {node:float('inf') for node in graph}
distances[start] = 0
heap = [[distances[start], start]]
while heap:
distance, destination = heapq.heappop(heap) # 3-3
for next_destination, next_distance in graph[destination].items(): # 3-4
new_distance = distance + next_distance
if new_distance < distances[next_destination]:
distances[next_destination] = new_distance
heapq.heappush(heap, [new_distance, next_destination])
3-4에서 목적지를 체크할 때 그 목적지를 방문하지 않아도 되는 경우가 있다. 바로 아래 그림처럼 목적지까지 다이렉트로 가는 간선의 거리가 조금 돌아서 가는 거리보다 더 멀 때이다.

1번 노드의 인접 노드 중 5번 노드는 직접 갈 때 보다 3번을 거쳐 가는 경우가 더 빠르다. 그리고 이미 3번 노드를 거쳐 5번에 도착한 이력이 있을 경우, 굳이 5번 노드를 체크할 이유는 없으므로 이 경우는 넘어간다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
import heapq
def djikstra(graph, start):
distances = {node:float('inf') for node in graph}
distances[start] = 0
heap = [[distances[start], start]]
while heap:
distance, destination = heapq.heappop(heap)
if distance > distances[destination]: # 3-5
continue
for next_destination, next_distance in graph[destination].items():
new_distance = distance + next_distance
if new_distance < distances[next_destination]:
distances[next_destination] = new_distance
heapq.heappush(heap, [new_distance, next_destination])
return distances
4. 원하는 거리 이하의 노드만 선택
노드별 거리 정보가 들어간 딕셔너리를 얻었으면 이 딕셔너리를 순회하면서 거리가 K 이하인 노드를 찾고 이 노드들 개수를 반환한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
def solution(N, road, K):
graph = create_graph(road)
distances = djikstra(graph, 1)
answer = 0 # 4
for destination, distance in distances.items():
if distance <= K:
answer += 1
return answer
Comment
다익스트라 알고리즘에 대해 길게 쓰여진 설명글들을 읽고 있으면 엄청 복잡해보이는데, 실제로 코드로 옮기고 나면 그렇게까지 복잡하지만도 않아서 놀랍다.
