Link
Introduction
거리두기가 코딩 테스트 문제의 주제로 까지 나오는 것 보면 코로나는 우리의 삶을 너무나도 크게 바꿔 놓은 것 같다. 설마 이 전염병이 이토록 길게 사람들을 고통스럽게 할 줄이야..
완전 탐색문제이다.
Note
- 기준점에서 1~2 거리에 있는 지점들을 모두 체크
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
DX = [ 0, -1, 0, 1, -2, -1, 1, 2, -1, 0, 1, 0]
DY = [-2, -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2]
def check_seats(place, x1, y1, x2, y2):
if x1 == x2:
return place[abs(y1+y2)//2][x1] == 'X'
elif y1 == y2:
return place[y1][abs(x1+x2)//2] == 'X'
else:
return place[y1][x2] == 'X' and place[y2][x1] == 'X'
def check_place(place):
for y in range(len(place)):
for x in range(len(place[0])):
for i in range(len(DX)):
x2, y2 = x + DX[i], y + DY[i]
if not 0 <= x2 < len(place[0]) or not 0 <= y2 < len(place) or \
place[y][x] != 'P' or place[y2][x2] != 'P':
continue
okay = check_seats(place, x, y, x2, y2)
if not okay:
return 0
return 1
def solution(places):
answer = []
for place in places:
result = check_place(place)
answer.append(result)
return answer
I. 필요한 함수 정의
구현할 내용은 간단하다. places에서 place를 하나씩 꺼내서 체크하고 결과 값을 정답리스트에 넣어준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
def check_place(place):
pass
def solution(places):
answer = []
for place in places
result = check_place(place) # 1-1
answer.append(result)
return answer
대기실을 체크를 하는 과정에서 두 좌석의 좌표를 주고 해당 좌석 두 개가 거리두기가 지켜졌는지를 체크하기 위한 함수 또한 정의해 준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
def check_seats(place, x1, y1, x2, y2):
pass
def check_place(place):
pass
def solution(places):
answer = []
for place in places
result = check_place(place) # 1-1
answer.append(result)
return answer
II. 함수구현 - 대기실 체크
대기실의 모든 칸을 순회한다.
1
2
3
4
5
def check_place(place):
for y in range(len(place)): # 2-1
for x in range(len(place[0])): # 2-1
pass
return 1
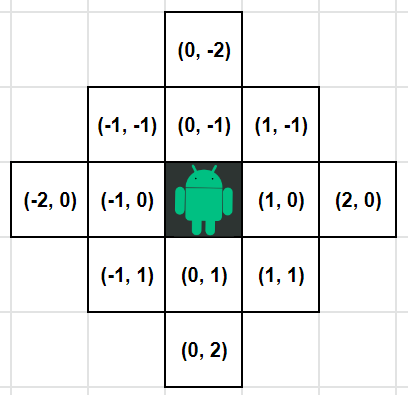
모든 칸을 순회하면서 현재 칸(x,y)의 근처의 거리 1~2 정도 떨어져 있는 모든 칸(x2, y2)을 체크 할 건데, (DX, DY)를 그림으로 표현하면 이런 느낌이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
DX = [ 0, -1, 0, 1, -2, -1, 1, 2, -1, 0, 1, 0] # 2-2
DY = [-2, -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2] # 2-2
def check_place(place):
for y in range(len(place)):
for x in range(len(place[0])):
for i in range(len(DX)):
x2, y2 = x + DX[i], y + DY[i] # 2-2
return 1
x2, y2가 대기실 칸의 범위에서 벗어나 있거나, 체크하려는 칸 둘 중 하나라도 응시자가 앉아있는 자리가 아니면 넘어간다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
DX = [ 0, -1, 0, 1, -2, -1, 1, 2, -1, 0, 1, 0]
DY = [-2, -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2]
def check_place(place):
for y in range(len(place)):
for x in range(len(place[0])):
for i in range(len(DX)):
x2, y2 = x + DX[i], y + DY[i]
if not 0 <= x2 < len(place[0]) or not 0 <= y2 < len(place) or \
place[y][x] != 'P' or place[y2][x2] != 'P': # 2-3
continue
return 1
두 좌석을 체크하고 거리두기가 지켜져 있지 않으면 0을 반환한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
DX = [ 0, -1, 0, 1, -2, -1, 1, 2, -1, 0, 1, 0]
DY = [-2, -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2]
def check_place(place):
for y in range(len(place)):
for x in range(len(place[0])):
for i in range(len(DX)):
x2, y2 = x + DX[i], y + DY[i]
if not 0 <= x2 < len(place[0]) or not 0 <= y2 < len(place) or \
place[y][x] != 'P' or place[y2][x2] != 'P':
continue
okay = check_seats(place, x, y, x2, y2) # 2-4
if not okay: # 2-4
return 0
return 1
III. 함수구현 - 좌석 체크
두 지점을 잡고 이 지점 두개가 유효한지를 판단하려면 아래의 조건을 체크 하면 된다.
- 둘 다 x값이 같은 경우, 그 사이 칸에 파티션이 있는지 체크한다.
- 둘 다 y값이 같은 경우, 그 사이 칸에 파티션이 있는지 체크한다.
- 나머지 경우엔 사이에 파티션이 모두 있는지 체크한다.
각 경우에 따른 파티션 ‘X’를 체크해준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
def check_seats(place, x1, y1, x2, y2):
if x1 == x2:
return place[(y1+y2)//2][x1] == 'X' # 3-1
elif y1 == y2:
return place[y1][(x1+x2)//2] == 'X' # 3-2
else:
return place[y1][x2] == 'X' and place[y2][x1] == 'X' # 3-3
Comment
탐색 문제는 과정이 머릿속에서 그려지기 때문에 재미있게 풀 수 있는 문제인 것 같다